GeneBio Systems
2x GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ Master Mix
2x GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ Master Mix
SKU:PCR-002-01
Couldn't load pickup availability
2x GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ Master Mix is a convenient ready-to-use mixture of GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ DNA polymerase, dNTP, buffer and magnesium ion. To set up a PCR reaction, you will only need to add the primers, the template and water.
For a brochure on this product, please follow this link.
GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ DNA polymerase was derived from Pfu DNA Polymerase, after several iterative rounds of protein engineering, the enzyme boasts the on-board unique extension factor, specificity-promoting factors and plateau-inhibiting factor. It is a Fast Pfu-derived polymerase.
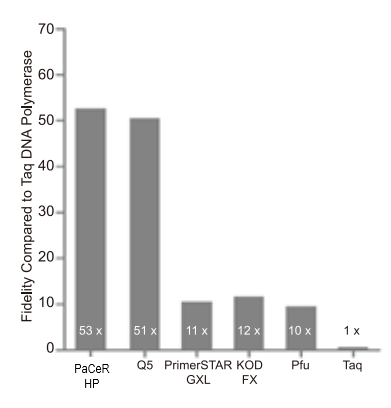
- Super Fidelity: 53-fold higher than Taq DNA Polymerase and 6-fold better than Pfu DNA polymerase
- Long Range capability: amplify fragments as long as 40 kbλ DNA, 20 kb genomic DNA and 10 kb cDNA
- Difficult PCR suitability: Amplify targets with as high as 85% GC
- Direct-PCR: resists inhibitors in crude lysates of bacteria, fungi, whole blood, cultured cells, plant tissues, etc.
- Superior Hot-Start enzyme, employing two MAb as molecular thermal switches of polymerase and proof-reading activities.
- Fast PCR: rate of synthesis more than 2x that of Taq DNA polymerase
In an internal comparison studies, GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ was compared in the following aspects with the leading all-round enzymes such as Phusion (Thermo) and eight other leading DNA polymerases for PCR:
- Success rate in amplifying human, mouse, rice, wheat, lambda and plasmid DNA, ranging in size from 305 to 14768 bp
- Sensitivity, i.e., ability to detect low copy templates,
- Speed of amplification with extension time as short as 1 s (for 450 bp) and 5 s (1135 bp)
- Amplification of High GC template with GC as high as 85%
GB-AMP™ PaCeR™ HP™ was clearly the best all-round enzyme for robustness, sensitivity, speed, high GC amplification and Direct PCR!
A tip on the use: The annealing temperature should be chosen based on the Tm values of the primers, in general, 55-65°C. See the user manual for details.
Looking for a similar DNA Polymerase with higher fidelity and amplification speed? Check out our 2× PaCeR (Phanta) Flash Master Mix (P510).
The enzyme generates blunt-ended products and thus products can be cloned by our Blunt End Cloning Kits.
Please note: If you are getting a low yield or even no amplification with PaCeR, please consider lowering the annealing temperature by 3-5 °C and/or increasing the annealing time (doubling). Talk to our Tech Support as you need.
Citations
- Nash D., et al. Hybrid sequencing reveals the genome of a Chrysochromulina parva virus provides insights into nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus evolution. BMC Genomics. 2025;26:534.
doi:10.1186/s12864-025-11700-z -
Dhaliwal J., Sharma P., et al. Protocol for the efficient and inducible generation of gene knockouts in Candida auris. STAR Protoc. 2024;5(3):102639.
doi:10.1016/j.xpro.2024.102639 - Deecker S.R., et al. Type I-F CRISPR-Cas distribution and array dynamics in Legionella pneumophila. G3 (Bethesda). 2020;10(3):1039–1050.
doi:10.1534/g3.119.400908 -
Hurst J.R., et al. Monkeypox virus shedding despite tecovirimat treatment. J Infect Dis. 2025; advanced online publication.
doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf471 - Monteiro1 VL et al. Ataxin-2 preserves oocyte genome integrity by promoting ribosomal RNA processing. bioRxiv. Posted June 16, 2025.
doi:10.1101/2025.06.13.659559 - Roscow O.M.A. Development of a full-length infectious clone of grapevine fanleaf virus and its application to study host-virus interactions. MSc Thesis. University of Guelph; 2019.
Available at: https://atrium.lib.uoguelph.ca/bitstream/10214/17655/3/Roscow_Olivia_201912_Msc.pdf -
Goetz J.A., et al. Exploring functional interplay amongst Escherichia coli efflux pumps. Microbiology (Reading). 2022;168(6):001233.
doi:10.1099/mic.0.001233